Muscle Injuries & Strains are common & understanding the type of strain you have can be as easy as 1, 2, 3! Muscle strains occur when muscle fibres are overloaded, causing rupture. The strain severity is classified into 3 grades (Grade 1 – Mild, Grade 2 Moderate & Grade 3 Complete muscle tear). To understand more…
Muscle Injuries & Strains – The most common source of muscle pain results from muscle strain due to overstretching. A muscle strain (also known as a pulled muscle or a muscle tear) varies in severity from mild to complete muscle rupture. Understanding muscle strains can assist in better understanding muscle-related injuries and pains.
Pathology and Histology
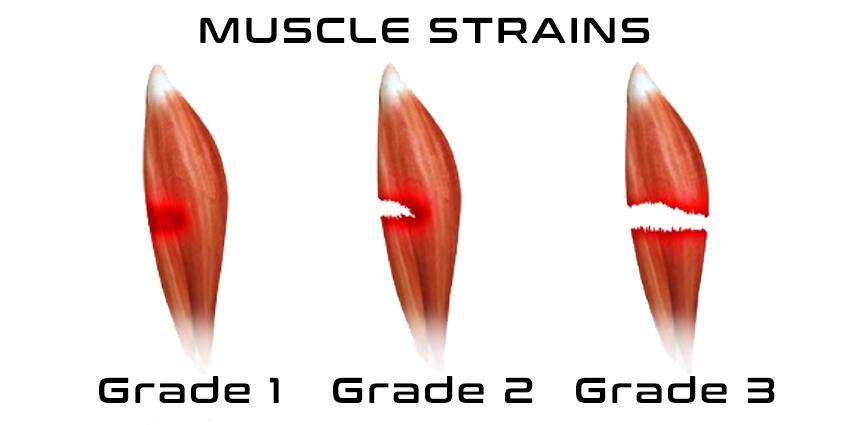
A muscle strain occurs when the muscle fibres are overloaded, causing rupture. The percentage of muscle fibres damaged involved and the severity of the tear determines the classification of the strain, broken down into 3 grades (Brukner & Khan, 2000).
Grade 1: Mild strain with little to no swelling and bruising. There is associated pain, however, strength and mobility are generally unaffected. Usually heals within 2-3 weeks
Grade 2: Moderate strain with symptoms of pain, swelling and bruising/discolouration. Strength, function and mobility are impacted. Usually heals within 2-3 months
Grade 3: Complete muscle tear with complete loss of function. Significant swelling, bruising and pain with visual deformities. Surgery is often performed, with a much longer rehabilitation process lasting up to 6 months.
Causes
A muscle strain or ‘pulled muscle’ occurs when a muscle is overstretched, overused or torn. This usually occurs due to fatigue or improper use of a muscle causing increased force being applied on the muscle that it cannot handle.
Diagnosis
Here at PROHEALTH PHYSIO, we provide an extensive clinical examination to determine the severity and the muscles involved. This includes looking into the history of the injury as well as objective findings related to range of motion, function, strength and clinical observation.
From this, a range of treatment strategies are developed to ensure that you get back to your sport, work or activities as soon as possible. Contact our friendly team to make a booking or discuss.
References
Brukner, P, Khan, K. Clinical Sports Medicine. 2nd ed. Sydney, Australia: McGraw-Hill; 2000.